Global Inflation – 4th Quarter 2021
Global inflation signals have persisted as elevated levels of consumer spending continue to collide with supply shortages across the world. It is likely that inflation will abate to some extent in 2022 as we expect supply side disruptions to be resolved to some extent.
Inflation is the continuous increase in prices over time. This represents the increase in the price of goods and services offered by a country. As inflation increases it conversely erodes the purchasing power of a country’s currency.
There are generally two types of inflation, cost-push, and demand-pull inflation. Cost-push inflation (decrease in aggregate supply) can occur from shortage of supply or due to increase in production cost (i.e., increase in wages or energy). Demand-pull inflation (increase in aggregate demand) is the result of increase in overall demand which can be generated from an increase in money supply or government spending among other drivers.
Current global inflation is as a direct consequence of both cost-push and demand-pull inflation.
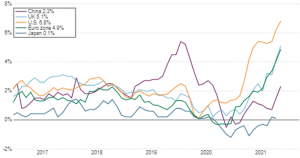
Global inflation surged in 2021 – U.S led major countries and regions in price spikes related to the pandemic
Source: Refinitiv via Reuters
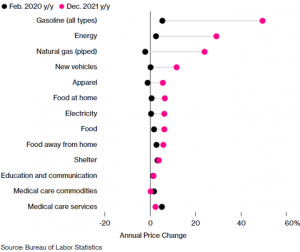
How it started, how it ended – US price changes since the start of the pandemic